
About
Warts
Safe and effective wart removal in Lucknow is available at The Velvet Skin Centre, Indira Nagar. Our skin doctor uses advanced methods for painless results and clear skin.
Book Appointment NowCall to book Appointment +91 8002558860

About
Safe and effective wart removal in Lucknow is available at The Velvet Skin Centre, Indira Nagar. Our skin doctor uses advanced methods for painless results and clear skin.
Book Appointment Now
Typical warts are small, grainy skin growths that often occur on your fingers or hands. Rough to the touch, common warts often feature a pattern of tiny black dots and clotted blood vessels, which are small.
Typical warts are generated by a virus and are transferred by touch. It can bring a wart as long as two to six months to form after your skin is uncovered to the virus. Typical warts are usually harmless and eventually vanish on their own. But multiple people dismiss them because they find them annoying or embarrassing.
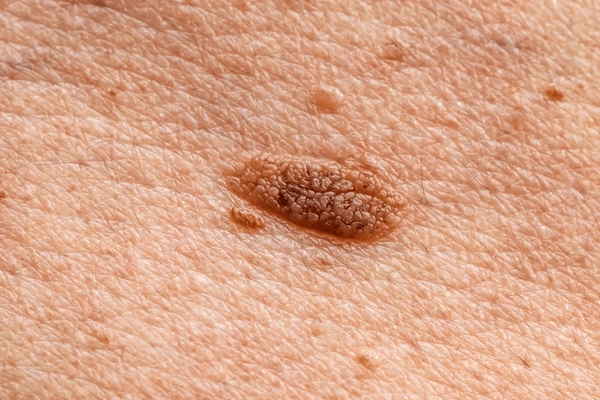
At The Velvet Skin Centre, Indira Nagar, Dr. Asma offers safe and effective wart removal in Lucknow. Warts caused by viral infections can spread and become unsightly if untreated. Using modern dermatological methods like laser therapy, cryotherapy, and topical treatments, we remove warts precisely and safely. Patients achieve smooth, healthy skin and freedom from recurring wart infections.
Warts are raised bumps on your skin generated by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They can be uncomfortable, contagious, and painful. There are home remedies, or you can see a medical professional for treatment.
Wart kinds vary hanging on the affected body part. Kinds include:
When the human papillomavirus (HPV) joins a cut in the skin, it provokes a skin condition that forms warts. Warts are very infectious. The virus can circulate from individual to individual or from additional regions of the body through:
Warts vary in appearance. They may look:
Your dermatologist can diagnose warts just by looking at the bumps. Occasionally, your doctor may carry a skin transition (biopsy) sample to test for HPV.
Warts often go away independently after your immune system fights off the virus. However, your doctor may recommend treatment because warts can spread, cause pain, and be unsightly. Options include:
About
About
With multiple skin and hair care clinics across Lucknow, including The Velvet Skin Centre led by Dr. Asma – the best skin doctor in Lucknow and a trusted hair specialist doctor in Lucknow – we make expert dermatological treatments easily accessible, ensuring you receive the best care close to home.
Phone: +91 8002558860
Phone: +91 8002558860
Phone: +91 8002558860

Copyright @ 2025 The Velvet Skin Centre All Rights Reserved